Gold advantages
Gold advantages
- It is the most malleable and ductile pure metal known , thus can be easily formed into thin coatings
- Gold does not rust, tarnish, corrode, crumble, decompose or decay, even after centuries on the sea floor or in a damp dripping cavern . That’s why it is called a "noble" metal
- Higher melting point (1,064.43°C) than silver
Gold disadvantages
- Very expensive in pure form
- Very high density , 19.32 grams per cubic centimeter at 293°K
Silver disadvantages
- Lower melting point than gold , only 961.78 °C
- Silver may be very ductile and malleablebut is slightly harder than gold
- Tarnishability of silver .Silver is stable in pure air and water, but tarnishes when it is exposed to air or water containing ozone or hydrogen sulfide to form a black layer of silver sulfide which can be cleaned off with dilute hydrochloric acid
- Very expensive in pure form
- Very high density
Silver advantages
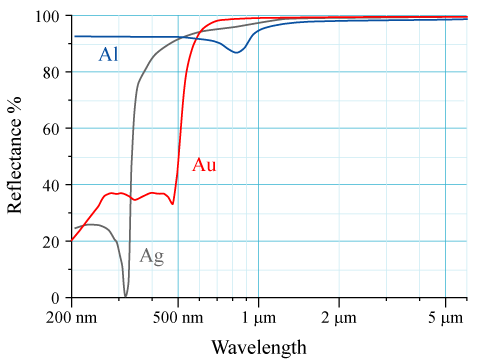
- It has the highest optical reflectivity although aluminium slightly outdoes it in parts of the visible spectrum, and it is a poor reflector of ultraviolet light
Aluminium
- It is much cheaper than gold or silver
- Low density , only 2.70 g·cm−3
- Aluminium is remarkable for its ability to resist corrosion due to the phenomenon of passivation due to a thin surface layer of aluminium oxide that forms when the metal is exposed to air, effectively preventing further oxidation . As a side effect that thin external layer of Al2O3 oxide negatively the metal's high reflectance ability . Generally Aluminium is one of the few metals that retain full silvery reflectance in finely powdered form, making it an important component of silver paints. Aluminium mirror finish has the highest reflectance of any metal in the 200–400 nm (UV) and the 3000–10000 nm (far IR) regions, while in the 400–700 nm visible range it is slightly outdone by tin and silver and in the 700–3000 (near IR) by silver, gold, and copper.
- It is not as malleable as gold or silver
So it is obvious why F1 mechanics chose gold for their needs